
There is no meaningful interpretation for the correlation coefficient as there is for the \(R^2\) value. Know what various correlation coefficient values mean.Know how to calculate the correlation coefficient r from the \(R^2\) value.Understand the cautions necessary in using the \(R^2\) value as a way of assessing the strength of the linear association.
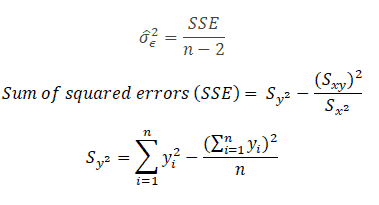
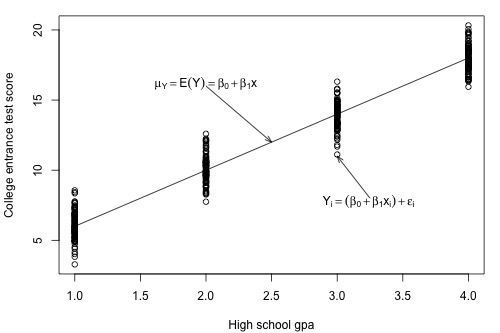
Know how to interpret the \(R^2\) value.That is, they can be 0 even if there is a perfect nonlinear association. Know that the coefficient of determination (\(R^2\)) and the correlation coefficient (r) are measures of linear association.Interpret the intercept \(b_\) from Minitab's fitted line plot and regression analysis output.Understand the concept of the least squares criterion.Distinguish between a deterministic relationship and a statistical relationship.The relationship between the dependent variable and each independent variable should be linear and all observations should be independent.Upon completion of this lesson, you should be able to: The variance of the distribution of the dependent variable should be constant for all values of the independent variable. Other assumptions: For each value of the independent variable, the distribution of the dependent variable must be normal.Categorical variables, such as religion, major field of study or region of residence, need to be recoded to binary (dummy) variables or other types of contrast variables. Data: Dependent and independent variables should be quantitative.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
